A common sleep aid restores healthier sleep patterns and protects mice from the brain damage seen in neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, according to new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The drug, lemborexant, prevents the harmful buildup of an abnormal form of a protein called tau in the brain, reducing the inflammatory brain damage tau is known to cause in Alzheimer’s.
The study suggests that lemborexant (better known by its brand name Dayvigo) and other drugs that work in the same way could help treat or prevent the damage caused by tau in multiple neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal syndrome and some frontotemporal dementias.
The study is published May 27 in Nature Neuroscience.
“We have known for a long time that sleep loss is a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease,” said senior author David M. Holtzman, MD, the Barbara Burton and Reuben M. Morriss III Distinguished Professor of Neurology at WashU Medicine. “In this new study, we have shown that lemborexant improves sleep and reduces abnormal tau, which appears to be a main driver of the neurological damage that we see in Alzheimer’s and several related disorders. We are hopeful this finding will lead to further studies of this sleep medication and the development of new therapeutics that may be more effective than current options either alone or in combination with other available treatments. (Continued below video…)
“The antibodies to amyloid that we now use to treat patients with early, mild Alzheimer’s dementia are helpful, but they don’t slow the disease down as much as we would like,” he added. “We need ways to reduce the abnormal tau buildup and its accompanying inflammation, and this type of sleep aid is worth looking at further. We are interested in whether going after both amyloid and tau with a combination of therapies could be more effective at slowing or stopping the progression of this disease.”
Holtzman and his team were among the first to identify the connection between poor sleep as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease and the buildup of proteins such as amyloid and tau. In past work studying mice genetically prone to amyloid and tau buildup characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease, they showed that sleep deprivation makes this buildup worse. Improving sleep in these mice with lemborexant appeared to be protective, the latest study showed, with less buildup of tau protein tangles and less nerve cell death associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
The protein tau accumulates in the brain in multiple neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s, and causes inflammation and the death of brain cells. Holtzman and his team — co-led by first author Samira Parhizkar, PhD, an instructor in neurology — tested lemborexant in part because it has effects in parts of the brain known to be affected by abnormal tau accumulation. It also does not impair motor coordination, which is a concern for people with dementia taking hypnotic sleep aids.
Lemborexant is one of three sleep drugs approved by the Food and Drug Administration that inhibit the effect of orexins, small proteins that regulate sleep, by acting as orexin receptor antagonists. Lemborexant blocks both orexin receptors (type 1 and type 2). Receptors are proteins on the cell surface that bind to other molecules and regulate cell activity. These receptors are known to play important roles in sleep-wake cycles and appetite, among other physiological processes.
The pharmaceutical company Eisai provided lemborexant for these studies as part of a research collaboration with WashU Medicine focused on developing innovative treatments for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases.
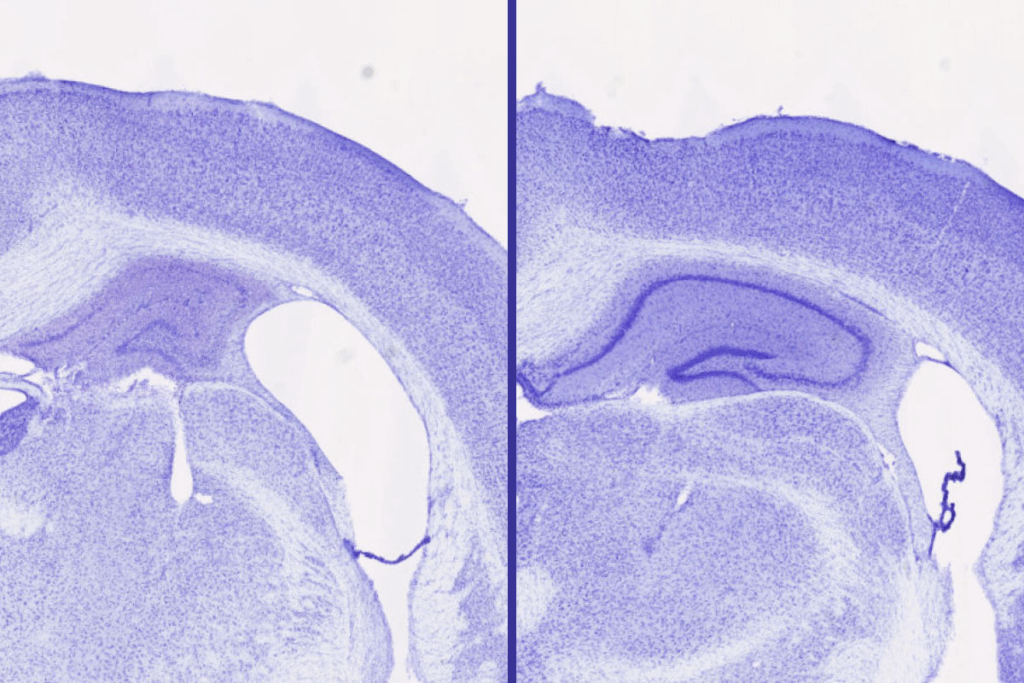
In mice genetically prone to harmful tau buildup, lemborexant reduced brain damage compared with control mice. For example, those receiving lemborexant showed 30% to 40% larger volume in the hippocampus — a part of the brain important for forming memories — compared with control mice and those receiving a different sleep drug, zolpidem, which belongs to a different class of drugs. Zolpidem increased sleep but had none of the protective effects against tau accumulation in the brain that were seen with lemborexant, suggesting that the type of sleep aid — orexin receptor antagonist — is key in producing the neuroprotective effects. The researchers also found that the beneficial effects were only seen in male mice, which they are still working to understand.
Normal tau is important in maintaining the structure and function of neurons. When healthy, it carries a small number of chemical tags called phosphate groups. But when tau picks up too many of these chemical tags, it can clump together, leading to inflammation and nerve cell death. The authors found that by blocking orexin receptors, lemborexant prevents excess tags from being added to tau, helping tau maintain its healthy roles in the brain.
Holtzman said his team is continuing to explore the reasons lemborexant treatment’s neuroprotective effects were seen only in male mice. He speculated that the sex discrepancy could be due to the observation that female mice with the same genetic predisposition to tau accumulation developed less-severe neurodegeneration compared with male mice. With less damage to begin with, potential beneficial effects of the drug could have been smaller and more difficult to detect.